One of the biggest diet fads around is – ‘Carbohydrates are bad for weight loss’.
A lot of diets suggest to completely remove carbohydrates (a.k.a carb) or reduce it extremely.
I am not saying that these diets are bad and won’t work. They certainly help you reduce weight but the problem is such diets are not sustainable.
For a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet is important. Carbohydrates have a lot of benefits and eliminating them will disturb normal body functions.
Also Read : Weight Loss and Carbohydrates
We all enjoy the carbohydrates in our meal, be it roti, idli, dosa, rice, sandwich, pasta, bread. But weight loss or fat loss becoming one of the major problems these days, we start blaming carbohydrates and try to cut down on carbs or completely go off it.
Over a period, low carb diets affect our body in more than one ways. Once we switch from these low carb diets to the regular diet, we tend to gain more weight than what we started off.
There seems to be a giant Carb-phobia going around among people, and they tend to believe that carbs are enemies for weight loss.
This post explains various topics related to carbohydrates –
- What are Carbohydrates?
- Benefits of Carbohydrates and why are they important to us?
- Simple (Fast Carbs) vs Complex carbs (Slow Carbs)
- Good vs Bad Carb Foods
- What is the Glycemic Index?
- What is the Glycemic Load?
- Foods and their Glycemic Index
- How much carb is required to lose weight?
- Common Questions around carbohydrates
What are carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for our body. Carbohydrates, a.k.a. carbs are basically the sugar, starch and fibres found in our food, fruits, grains, vegetables and milk products.
Carbs are one of the 3 essential macronutrients for our body – Protein, Carbohydrates, Fat.
At chemical combination level, they are made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, hence the name carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are the molecules that the body breaks into sugar and which is then produces energy.
Researchers have shared that for a normal individual, 45-65% of calorie requirement should be met from carbs. Going below suggested levels hampers productivity in daily life and causes mood swings.
One gram of carbohydrate equals 4Calories. If, for example, your daily calorie requirement is 1800Calories, then you must be consuming 200-292gm of carbs per day. The daily requirement may defer based on your goal but it should be around this range.
Many of the weight loss diets recommend reducing carbs, though reducing carbs below required levels can cause damage to day-to-day body functions. Some of the athletes go on extremely low carb diets to achieve certain goals, but such diets are not recommended for a long period.
Benefits of Carbohydrates and why are they Important to us
Carbohydrates, as mentioned above, are the fuel provider for our central nervous system and our energy for physical activities.
Here are benefits of carbohydrates –
1. Regulates mood
Low blood sugar levels induce mood swings and irritation. Consuming carbohydrates normalizes the sugar levels.
Have you noticed when you are very hungry, you feel loss of energy and concentration or even feel agitated. This is primarily caused by low sugar levels which is brought back to normal by consuming required amount of carbs. (Read below for how carbs fix sugar levels)
In addition, carbs trigger the production of serotonin, widely knows as happiness hormone. Extremely low levels of serotonin results in depression and other mental illness.
2. Helps gain muscles
Bodybuilders looking to gain muscles and bulk up rely a lot on carbohydrates. Consuming carbs along with protein helps muscle recovery and amino acid synthesis.
Read to know more about how to gain lean muscle.
3. Improve athletic performance
Carbs are important for individuals performing heavy physical activities, be it athletes, runners, bodybuilders or other sports.
Proving as an efficient source of energy, carbs help in attaining the peak physical performance levels.
4. Prevent Weight Gain and Promotes Weight Loss
The fibres in carbohydrates are extremely slow digesting or say indigestible. Consuming carbs that are high in fibre keeps us full for longer and stops from binging.
Fibres also absorb a lot of water, which improves your water intake and in turn the digestive system.
In totality, appropriate fibre intake helps weight loss.
5. Helps Relieve Muscle Fatigue
Bodybuilders state ‘Carbs are Bae’. Post workout muscle fatigue is very common. Carbs play an important role in muscle recovery. They replenish the lost glycogen in the muscles and help muscle growth. Read this to know more about the role of carbohydrates in recovery.
Simple (Fast Crabs) vs Complex carbs (Slow Carbs)
Carbs are mainly divided into two categories – simple carbs and complex carbs. The major differentiator between these two carbs is their fibre content.
Confusing? Let’s begin with understanding how carbs are absorbed in the body.
Brief Explanation – Digestion of Simple vs complex carbs
Based on the structural details of a carbohydrate molecule, it can be put in the category of – simple or complex carbs.
Simple carbs are simple sugar molecules that are easy to break by our body’s digestive system. Though, complex carbs contain high amount fibre which takes longer to break down. This is why complex carbs are also known as Slow Carbs.
Once the carbs are broken into sugar molecules, they get absorbed by our bloodstream, spiking the blood sugar level. Our body cells absorb the glucose from the blood and the excess glucose deposits in cells in the form of glycogen or fat.
Simple carbs get absorbed almost immediately by our body and hence produce high energy as soon as they are digested. If the body is not able to utilize all the sugar at that time, the excess sugar gets stored in cells as fat.
Now, since complex carbs take longer to break, and the sugar is released slowly in the body. This way, the body gets enough time to absorb the energy produced by the sugar molecules. Hence, decreasing the chances of the sugars converting to fat.
Detailed Explanation – Molecular structures and digestion of simple and complex carbs
Carbohydrates are sugar molecules, which can be – simple or complex in their molecular structures.
Simple carbs = Monosaccharides or Disaccharides
Simple sugars, referred to monosaccharides, are glucose, fructose or galactose molecules. These are called monosaccharides because they are single molecules of any of these sugar types.
When two molecules are combined, they are called disaccharides. Eg. Lactose, Maltose and Sucrose.
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Complex carbohydrates are linked sugars with more than 3 sugars.
Complex sugar = Oligosaccharides or Polysaccharides
Oligosaccharides = 3-10 Linked Sugars
Polysaccharides = More than 10 Linked Sugars
While digesting the carbs, the body breaks down the linked sugars molecules to their building blocks of simple sugar.
Now, this is where the difference comes into the play. The way these molecules are linked in simple carbs (starch) or in complex carb (fibre) are different.
The linkages in simple carbs are easily broken and the sugar gets dissolved in the blood very quickly. While complex carb linkages are hard to break into simple sugars and take longer to get into bloodstreams.
When carbs are broken down into sugars, which goes into blood, the blood sugar levels increase. These sugar molecules are then absorbed in tissues to be converted to energy and used in body functions.
Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, helps sugar molecules gets absorbed in muscle tissues. If body’s insulin sensitivity goes down, the sugar molecules don’t get absorbed in the muscle tissues and hence the insulin and sugar levels of blood streams rises.
Consuming high quantity of foods that spike blood sugar levels, tend to hamper the insulin sensitivity as well. And this eventually causes sugar conversion into fat.
Good vs bad carb foods
Carbs are found in vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes and dairy products. Whole foods are good because of their fibre content.
The foods like cakes, doughnuts, aerated drinks, processed foods are refined food and contain a high amount of refined sugar and very low amount of fibre. These are certainly bad carb food. They offer sheer calories and no nutritional values.
Choosing complex carbs over simple carbs is all the change required to shift to a healthy lifestyle.
Good carb foods –
- Don’t contain in refined sugar or grains
- Provide high fibre
- Are low in saturated fat and high in nutrients
Bad carb foods –
- High in refined grains and sugar
- Hardly contain fibres
- Provide sheer calories and no nutritional values
What is the Glycemic Index
Glycemic index (GI) is the factor by which the carbohydrates get converted to Glycogen in our body. This means that the foods like simple carbs are high GI since they release sugar fast and excessive sugar converts in glycogen.
Low GI foods like complex carbs, take longer to digest completely and hence result in lower probability of sugar converting to Glycogen.
Glycogen is the enemy that causes fat accumulation. The higher the GI, higher are the chances of you gaining fat deposition from that food.
High GI carbohydrates are best consumed immediately after a high-intensity workout or a long sprint. When the body needs quick recovery, and high GI foods come in handy to help. Apart from those instances of high energy requirement, it’s advised to consume low GI foods like vegetables, fruits and whole grains.
If you are looking for fat loss or maintaining the body-fat, try consuming more of low GI food. It’s good to avoid high GI food, especially in late evenings when our energy requirements are minimal and our metabolism is slow.
What is the Glycemic Load
Low GI foods are good but how much you should be consuming them? Can you eat any amount of low GI food and not gain fat?
NO!
This brings us to Glycemic Load – Multiplying GI of your food with the food quantity gives Glycemic Load of your food intake.
Glycemic Load (GL) = Glycemic Index (GI) * Quantity of Food
Considering only GI of food is not complete information. What we need to consider is GL of the food.
The fact is – Not Glycemic Index, but Glycemic Load is the real culprit that causes Glycogen in your body and intern fat accumulation.
If you are eating low GI foods but in high quantity, the overall Glycemic Load of your meal is going to be high. This might even cause the same damage as eating high GI food.
Consuming high quantity of slow carbs or low GI foods like brown rice, steal cut oats and legumes can result in weight gain due to high Glycemic Load of your meal.
The advised quantity of carbohydrates is about 45-65% of your complete calorie requirement. Do ensure consuming within given limits.
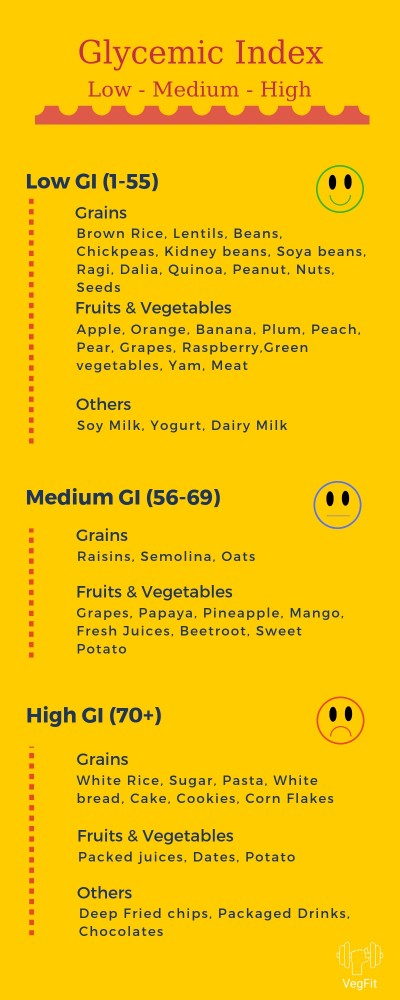
Foods and their Glycemic Index
Based on the Glycemic Index, you can very well choose the food to eat or avoid depending on your goals.
Foods like sugar, cakes, carbonated drinks and doughnuts are amongst the highest Glycemic index range. These foods contain simple sugar which almost immediately spikes up your blood sugar levels, resulting in higher fat storage.
Vegetables and high protein foods are on the lowest spectrum of GI. They keep you full for longer and hardly impact your blood sugar levels.
The glycemic index ranges from 1 to 100, where 100 is the highest GI which is of glucose or sugar.
Foods with a GI (glycemic index) below 55 are low GI foods. A GI of 56 to 69 is medium, and high glycemic index foods have a value of 70 or more.
Below infographic lists popular foods that fall in Low, Medium and High GI categories. This can be helpful for your everyday choice of food. It will be a good idea to print it and keep it in your kitchen or paste it on fridge. This will constantly remind you of right foods to choose, especially when you looking to change your carb selection.
How much carb is required
Everyone has a different calorie or macro requirement. Though, researchers suggest a certain range of carbohydrate requirement for all the adults. Here is what Reid Health Organisation quotes :
According to Reid Health
Most adults get 45 to 65 percent of their calories from carbohydrates. Since carbohydrates contain four calories per gram, you should consume 225 to 325 grams of carbohydrates on a daily basis if you’re following a 2,000-calorie diet. Recommended consumption of carbs is 130 grams for adults, 175 grams for women who are pregnant and 210 grams for women who are breastfeeding.
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010, women should consume 25 grams of fiber on a daily basis, while men should consume 38 grams of fiber on a daily basis.
Source: Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010, United States Department of Agriculture
Based on what your fitness goal is, carbohydrate requirement will vary. It also depends on how well our body is able to process carbs. As a baseline, there are different macro ratios that you can follow and experiment what suits you : Low carb, Med Carb and High carb. Here is a tool that can help you calculate your macro requirement :
BMR and Macros calculator : Squats.in/tools
Common Questions around Carbohydrates
1. Is it ok to consume fruits while trying to lose weight?
Yes. Fruits contain a lot of fibres and are good carbs though their quantity should be controlled to keep the overall calorie consumption in limits.
2. Can I take white rice while trying to lose weight?
Yes, occasionally. Since white rice is a type of simple carbs, it should be consumed in moderation and not during late evenings. It is preferred to replace it with brown rice to consume more fibres.
4. How about consuming fresh fruit juice?
Fruits juices are basically fruits without the fibre. Drinking fruit juice is like drinking sugar. Yes, you will be consuming vitamins and minerals of the fruit but the damage done by taking the pulp out is more than a few grams of vitamin consumption.
Fruit juices should be consumed when you are looking for a quick energy source.
5. How many calories do I need per day?
If you are healthy and do moderate workout 2-3 days a week, you can roughly calculate your calorie requirement by multiplying your body weight in kg with 31. For eg. if you weigh 60Kg, then your maintenance calorie require would be 1860Calorie.
Disclaimer: This will only give a rough estimate as a starter. Calorie requirement depends on your age, weight, workout intensity and of course your gender.
For a detailed and more accurate calorie calculation, try this calorie calculator tool.
6. How much fibre do I need to consume per day?
Fibre is the one of the most IMP element in carbs. An adult requires around 23-30gm of fibre per day. For vegetarians, reaching the goal is very easy since most of the veggies contain a lot of fibre.
Do ensure not overdoing it since excessive fibre might cause constipation.
7. How can I add more fibre in my diet?
Include foods in your diet that contain high fibre like, vegetables, brown rice, quinoa, whole grains.
Tip: If for some reason you are not able to meet your daily fibre requirement, include psyllium in the diet.
8. Shall I replace carbonated drinks with zero-calorie diet drinks, since they don’t contain sugar?
Well, it’s a very debatable topic. When you look at calorie intake, certainly zero calorie or diet drinks have lot fewer calories than normal drinks. If you are looking to lose weight and just can not live without a carbonated drink, you can take 1-2 cans a week.
But, are these packaged drinks healthy? NO. The sugar substitutes used in them cause long-term health issues. And a lot of experiments have proved that the people who consume aerated drinks are more prone to get fat than the ones who don’t.
9. Are packaged juices healthy?
NO. Juices are simple sugar. If you are looking for weight loss, avoid fruit juices completely. Fruits are good to consume in moderation since they come with a lot of fibre and also kill your sweet craving.
Packaged juices, on the other hand, offer no benefits of fruits and contain ample sugar and additives. These should be avoided totally.
10. How do I avoid food craving ?
“Any dietary change that cuts calories or familiar foods will inevitably leave you vulnerable to cravings, often for whatever’s ‘off limits.’ It’s just human nature,” explains Jenna A. Bell Wilson, Ph.D., R.D. But there are two things you can do.
First, when you decide to satisfy a craving, take time to enjoy the food and don’t feel guilty about it. For foods you can’t stop eating once you get started, try having them only in situations where the portion is controlled. For instance, eat them at a restaurant or buy single-serving items rather than a whole package.
Most weight maintainers say that they avoid buying highly tempting foods but that if they do have such foods around, they keep them out of sight and therefore out of mind.
Here you can learn certain habits, practicing who will help you avoid craving for unhealthy food – 8 Habits to Avoid Craving for Unhealthy Food.
If you have more questions around carbohydrates or how they should be consumed while losing weight or gaining muscles, do share them in comment section below and I will certainly include them in the article for benefits of others.